Foreword
QCVN 05 : 2020/BCT is developed by the Drafting Team; submitted by the Vietnam Chemicals Agency for approval; appraised by the Ministry of Science and Technology; promulgated together with the Circular No. 48/2020/TT-BCT dated December 21, 2020 by the Minister of Industry and Trade.
NATIONAL TECHNICAL REGULATION ON SAFETY IN PRODUCTION, COMMERCE, USE, STORAGE AND TRANSPORTATION OF HAZARDOUS CHEMICALS
This Regulation provides for general requirements concerning safety in production, commerce, use, storage and transportation of hazardous chemicals in the field of industry.
This Regulation applies to organizations and individuals that produce, trade, use, store and transport hazardous chemicals in the field of industry.
3. Definitions and abbreviations
For the purposes of this Regulation, the terms and abbreviations below shall be construed as follows:
3.1. “GHS” means the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals.
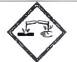
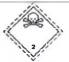
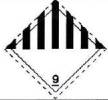
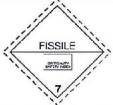
3.2. “pictogram” means a graphical composition that conveys information about physical, health and environmental hazards according to the GHS and is indicated by GHS01; GHS02; GHS03; GHS04; GHS05; GHS06; GHS07; GHS08; GHS09. GHS pictograms are specified in the Annex A of this Regulation.
3.3. “hazardous chemical” means a chemical that has one or more of the following hazardous properties based on GHS Hazard Classification: explosivity; strong oxidation; strong corrosion; flammability; acute toxicity, chronic toxicity; irritation; carcinogenicity or potential carcinogenicity; causing genetic defects; reproductive toxicity; bioaccumulation; persistent organic pollution; toxic to the environment.
3.4. “MSDS” means the Material safety data sheet.
3.5. “containers” include packages, bottles, tanks or containers used to store goods.
1.1. QCVN 03: 2019/BYT- National Technical Regulation on Permissible Exposure Limit Value of 50 chemicals at the Workplace.
1.2. QCVN 40: 2011/BTNMT - National Technical Regulation on Industrial Wastewater.
1.3. QCVN 19: 2009/BTNMT - National Technical Regulation on Industrial Emission of Inorganic Substances and Dusts.
1.4. QCVN 20: 2009/BTNMT - National Technical Regulation on Industrial Emission of Organic Substances.
1.5. QCVN 06: 2020/BXD - National Technical Regulation on Fire Safety of Buildings and Constructions.
1.6. QCVN 0326: 2016/BYT - National Technical Regulation on Microclimate - Permissible Value of Microclimate in the Workplace.
1.7. QCVN 22: 2016/BYT - NATIONAL TECHNICAL REGULATION on Lighting - Permissible Levels of Lighting in the Workplace.
1.8. TCVN 4604: 2012 - Industrial enterprises - Production building - Design standard.
1.9. TCVN 2290: 1978 - Manufacturing equipment - General safety requirements.
1.10. TCVN 3255: 1986 - Explosion safety- General requirements.
1.11. TCVN 6304: 1997 - Liquefied petroleum gas cylinders - Safety requirements in storage, handling and transportation.
2. Requirements concerning documents, boards and signs
Factories, warehouses and areas with activities related to hazardous chemicals must have the following documents, boards and signs:
2.1. Chemical safety rule boards, which should be placed at entrance doors in noticeable positions.
2.2. Diagrams indicating locations of storage locations, pipes, belt conveyers transporting hazardous chemicals, locations of personal protective equipment (PPE) and chemical incident response kits and medical devices, escape routes, evacuation assembly points of factories, warehouses and areas, which should be placed at the entrance doors in noticeable positions;
2.3. Signs suitable for the degree of hazard of chemicals, which should be put up in noticeable positions in every hazardous chemical storage area and handling area. Signs must indicate hazardous properties of chemicals and contain at least the following information: pictograms, signal words and hazard statements. In case chemicals have different hazardous properties, hazard signs must fully show these hazardous properties.
Hazard signs must be designed in such a way that pictograms thereon are easily recognizable from a distance of 5 m.
Pictograms, signal words and hazard statements shall comply with the Circular No. 32/2017/TT-BCT on elaboration of certain Articles of the Law on Chemicals and the Government’s Decree No. 113/2017/ND-CP dated October 09, 2017 on elaboration of certain Articles of the Law on Chemicals or applicable regulations on classification and labeling of chemicals;
2.4. Escape plans, which should be placed in every hazardous chemical storage and handling areas and high incidence areas in such a way that workers are able to read them at the workplace and on escape routes.
An escape plan must show the following information: appropriate escape routes, locations of personal protective equipment, incident response kits and medical devices;
2.5. Chemical incident response procedures and lists of chemicals and MSDSs, which should be placed in noticeable and accessible positions. A list of chemicals must contain information about chemicals’ names and trade names, classification, pictograms, maximum quantities stored at a time and storage areas.
3. Requirements when working and coming into contact with hazardous chemicals
3.1. Persons who work and come into contact with hazardous chemicals must be trained in chemical safety in compliance with regulations of the Government’s Decree No. 113/2017/ND-CP dated October 09, 2017 on elaboration of certain Articles of the Law on Chemicals, and applicable regulations.
Facilities that have hazardous chemicals shall provide training in chemical safety and occupational hygiene to their employees.
3.2. Measures should be in place to control entry and exit to factories and warehouses containing hazardous chemicals and a list of persons present in areas should be provided to the rescue force in the event of a chemical incident.
3.3. Hazardous chemical facilities must disseminate and provide guidance on safety rules, and supply appropriate PPE to visitors to the facilities.
3.4. Every hazardous chemical facility must fully provide its workers with PPE appropriate to the degree of hazard of each chemical and to the nature of their work. Such PPE must be kept in good condition;
It is required to inspect PPE at least once a month to ensure that there is an adequate supply of PPE that should be readily available. The inspection record shall be retained within 12 months and presented to the competent authority upon request.
3.5. Every hazardous chemical facility must satisfy the requirements concerning permissible exposure limit value of 50 chemicals at the workplace prescribed in QCVN 03:2019/BYT and applicable regulations on occupational safety and hygiene.
4. Requirements for chemical incident response and environmental protection
4.1. Every hazardous chemical facility must formulate and implement a plan or measure to prevent and respond to chemical incidents in accordance with applicable regulations.
4.2. Only those who have a good understanding of the hazards of chemicals, the incident response procedures, the response method methods, and are provided with adequate PPE are allowed to participate in the incident handling.
4.3. Hazardous chemical facilities must fully comply with regulations of law on environmental protection. Waste must be treated in accordance with QCVN 40: 2011/BTNMT and emissions must be treated in accordance with QCVN 19: 2009/BTNMT and QCVN 20: 2009/BTNMT.
5. Requirements concerning factories and warehouses
5.1. The design, construction and renovation of factories and warehouses containing hazardous chemicals (hereinafter referred to as “factories and warehouse”) shall comply with the regulations set out in QCVN 06: 2020/BXD and TCVN 4604: 2012, and other relevant regulations of law, and shall be suitable for the nature, scale and technologies for manufacturing and storing chemicals.
5.2. Escape routes of factories and warehouses must be designed and constructed in accordance the regulations laid down in QCVN 06: 2020/BXD and applicable regulations.
5.3. Air ventilation systems of factories and warehouses must be installed in such a manner as to ensure that the permissible value of microclimate in the workplace specified in QCVN 26: 2016/BYT is not exceeded.
5.4. Lighting systems of factories and warehouses must be built in such a manner as to maintain the permissible levels of lighting in the workplace specified in QCVN 22: 2016/BYT.
5.5. Factories and warehouses must have lightning protection systems or be situated in lightning protection areas and periodically inspected according to applicable regulations.
5.6. Factories and warehouses must undergo annual inspections of safety and safety assurance measures before the rainy season. The inspection record must be retained until the next inspection.
5.7. Floors of factories and warehouses must withstand loads and chemical corrosion, and be non-slip.
5.8. Factories and warehouses must have at least 2 entrances and exits. Entrances, exits, emergency exits and walkways should not be obstructed.
5.9. Factories and warehouses must install emergency eyewash and shower equipment which should be placed with 10 m (but not closer than 2 m) to hazardous chemical handling area.
5.10. Warehouses must be divided into each specific area by the properties of each chemical type and group.
5.11. Incompatible chemicals must be stored in an area at a safe distance or segregated in areas separated by a physical wall to ensure that they cannot come into contact with one another even if an incident occurs. The incompatible chemicals are provided in the Annex B of this Regulation.
5.12. Chemicals must be so arranged in the warehouse that safety of workers and goods is ensured. To be specific:
- Regarding bagged goods, they must be placed on pedestals or racks, at least 0.5 m from the wall, water reactive chemicals must be placed on pedestals at a height of at least 0.12 m;
- Equipment containing chemicals should not be placed too close to the warehouse’s ceiling and at a height of more than 2 m if stacks are not available;
- The primary aisle of the warehouse must be at least 1.5 m wide;
- A plan should be in place to inspect and supervise areas where there is a risk of an incident occurring in every factory and warehouse.
5.13. When placing chemicals on stacks, racks, cabinets, etc. containing chemicals, ensure that the permissible design load and permissible load of the floor are not exceeded.
5.14. Chemical containers must be stacked in such a manner as to ensure that the permissible load capacity of a pallet is not exceeded. Containers with a capacity of less than 1,000 liters and over 1,000 liters must not be stacked more than three (03) and two (02) tiers high respectively.
5.15. Factories and warehouses containing liquid hazardous chemicals must have a system of absorption banks and trenches to ensure that: chemicals do not escape to the environment; chemicals do not come into contact with reactive chemicals in the event of spills or leaks of other hazardous chemicals.
5.16. Areas storing spilled chemicals, discarded chemicals, used packages and storage equipment, and expired chemicals must comply with regulations on environmental protection and hazardous waste management.
6. Requirements concerning equipment
6.1. Equipment for production, storage, transport and use of hazardous chemicals must comply with general safety requirements specified in QCVN 2290: 1978.
6.2. When replacing or adding parts of the abovementioned equipment, it is required to ensure mechanical resistance, chemical resistance, fire resistance, thermal resistance and tightness according to the prescribed specifications.
6.3. Equipment for transporting chemicals (belt conveyors, lifting conveyors, etc.) must have a pre-start warning system.
6.4. Hot surfaces of chemical-containing equipment and pipes which might cause burns to workers must be kept covered.
6.5. When operating and using chemical-containing equipment under pressure, it is required to comply with the requirements laid down in technical regulations on pressure equipment and applicable regulations.
6.6. The system for measuring and controlling equipment during the production of hazardous chemicals must undergo periodic inspection and calibration to ensure their stable operation.
7. Requirements concerning containers and goods labels
7.1. Hazardous chemical containers must be tight and sturdy, and withstand shocks and weather impacts during the transportation and movement of goods between vehicles and loading and unloading of goods onto factories and warehouses by manual means or by machine. The loading levels must be conformable with regulations applicable to each type of hazardous chemical. Used packages must be separately stored. Used packages must be cleaned before being reused to ensure no reaction with the next chemicals to be loaded.
Covers must be marked to distinguish one chemical from the others.
7.2. Hazardous chemical containers must bear labels showing sufficient information in accordance with applicable regulations on chemical labeling.
7.3. A chemical label must be easily legible and tear resistant. If the label is lost or damaged resulting in it not clearly indicating the chemical in the container, it an analysis shall be carried out to identify the name and primary contents of the chemical to attach a new label before it is sold or used (even in the case of compulsory destruction).
Any facility that produces, trades, uses or stores flammable and explosive chemicals satisfying the labeling criteria corresponding to any of the pictograms GHS01, GHS02, GHS03, GHS04 (hereinafter referred to as “flammable and explosive chemicals”) must comply with the following requirements:
8.1. Requirements for arranging and placing chemicals
8.1.1. Warehouses of flammable and explosive chemicals must be isolated from fire and heat sources.
8.1.2. The minimum safe distance from a flammable chemical storage area to a source of heat or ignition is specified in the table below:
| From storage area to another area | Minimum safe distance (m) |
| Area for storage of flammable liquids inside closed containers | 3 |
| Area for storage of flammable liquids being decanted and stirred | 8 |
Facilities having flammable and explosive chemicals may maintain a greater safety distance depending on heat generation risk assessment and fire incident precautions.
8.1.3. Flammable and explosive chemicals must not be stored together with oxygen, oxygen-release substances, hazardous and incompatible chemicals, substances subject to different fire extinguishing requirements or substances capable of triggering hazardous reaction in the case of contact or fire.
8.1.4. Equipment and pipes containing flammable or explosive chemicals must not be placed near heat sources. In the case of exposure to direct sunlight, measures should be adopted to reduce heat (coating reflective paint or spraying water, etc.);
8.2. Requirements concerning electric power systems and air ventilation systems
8.2.1. An electric power system in areas where flammable and explosive chemicals exist must satisfy the following requirements:
- Power tools, electrical equipment and lighting equipment must be fire and explosion safe and the explosion-proof level of which must be relevant to the environment of flammable or explosive vapor or gas;
- Power cables must not be laid in the same underground trench or location where pipes conveying flammable and explosive vapors, gases and liquids exist;
- Circuit breakers and outlets must be located outside areas where flammable or explosive chemicals exist;
8.2.2. Air ventilation systems of warehouses of flammable and explosive chemicals must provide adequate ventilation in such a way that the chemical vapor concentration is less than 10% of the lower explosive limit either by natural or mechanical means;
8.3. Requirements concerning equipment, tools and containers
8.3.1. Machinery and equipment in areas where flammable chemicals exist must satisfy fire safety requirements under TCVN 3255: 1986. Technical measures should be taken to ensure that tools working in areas where flammable and explosive chemicals exist do not produce any friction or impact spark.
8.3.2. Electrical tools and equipment, and lifting equipment installed and used inside warehouses must be fire and explosion proof.
- Lifting equipment and forklifts must satisfy applicable fire safety standards. Repair, refueling and charging are prohibited in chemical warehouses and factories producing and using chemicals.
- Tools used to open flammable and explosive chemical containers must be made of materials that do not produce any friction or impact spark or technical measures should be taken to avoid producing friction or impact sparks.
8.3.3. Containers of flammable and explosive liquids must maintain the prescribed filling factor depending on the physico-chemical properties of such liquids; large containers must be equipped with an one-way relief valve or flame failure device with an explosion-proof flange; the explosion-proof flange must be made of non-flammable and explosive materials; the end of a pipe conveying flammable and explosive chemicals to a container must be close to the edge or to the bottom; Pressure vessels must have overpressure relief valves.
Containers must be inspected at least once a month. The inspection record must be retained until the next inspection and presented to the competent authority upon request.
8.3.4. Flammable and explosive containers which are exposed to sunlight must be made of light-blocking materials or covered with light-blocking materials. Glass doors of warehouses must be painted to block light or use frosted glass;
8.4. Requirements when working and coming into contact with chemicals
8.4.1. Compressed air that contains oxygen must not be used to propel flammable or explosive chemicals from one device to another. When decanting flammable or explosive chemicals from one bottle to another, both bottles must be grounded;
8.4.2. A solvent and a liquid chemical in open equipment must be mixed at a distance of at least 10 m away from the fire. Only mix a solvent with a liquid chemical when the temperature of the liquid chemical is lower than the boiling point of the solvent.
8.4.3. A flame must not be used as source of light to find the leaks of pipes or equipment containing flammable or explosive chemicals;
8.4.4. If flammable or explosive chemicals come into direct contact with other chemicals, the following requirements must be satisfied:
- The technology process and safe operating procedure are strictly followed;
- The effects of additional substances on the thermotolerance, flammability or explosivity of flammable or explosive chemicals are known;
- No unidentified impurities are present in the additional substances.
8.4.5. Before welding equipment and pipes that are previously used to contain flammable or explosive chemicals, it is required to open all equipment covers and pipe flanges to completely release flammable or explosive vapors and clean them in such a manner as to ensure that no flammable or explosive mixture is formed.
8.4.6. Before introducing a flammable or explosive substance into a pipe or equipment or before and after repair, the fire safety procedure must be strictly followed:
- Conduct a leak test or pressure test (if necessary);
- Use a suitable solvent or inert gases to clean;
- Determine the remaining content of oxygen, air or combustible/explosive substance so that a flammable/explosive mixture cannot be formed.
The inspection result must be certified by a safety officer before carrying out repair;
8.4.7. When doing spray painting, especially in a closed space, it is required to ensure that the mixture of paint and air is beyond the explosive limit and to avoid static electricity causing fire and explosion;
8.4.8. When loading and unloading flammable or explosive chemicals, it is required to:
- Establish a procedure for safe loading and unloading of flammable or explosive chemicals;
- Equip appropriate facilities for spill response;
- Prohibit unauthorized transport vehicles or transport vehicles that fail to satisfy fire safety regulations from entering flammable and explosive chemical storage areas.
- During the loading and unloading of flammable and explosive chemicals, transport vehicles must be completely turned off or take appropriate fire safety measures;
8.4.9. In the event of a fire or explosion incident, every person that is present must use PPE to participate in the rescue and fire fighting. Persons who do not have appropriate PPE are not permitted to participate in fire fighting. The person who calls the fire department and ambulance services must provide specific address and directly lead the way.
8.4.11. When a fire occurs in the area where a ventilator is operating, the ventilator must be stopped to avoid spreading the fire, then take appropriate extinguishing measures.
8.4.12. There must be stringent regulations on the use of fire shall be imposed where explosive or flammable chemicals are produced, used or stored. When carrying out mechanical repair, arc welding or oxy-fuel welding, the fire safety procedures must be followed with certification by an occupational health and safety officer.
9. Requirements for production, commerce, use, storage and transportation of corrosive chemicals
Any facility that produces, trades, uses or stores corrosive chemicals satisfying the labeling criteria corresponding to pictogram GHS05 (hereinafter referred to as “corrosive chemicals”) must comply with the following regulations:
9.1. Requirements concerning equipment, factories and warehouses containing corrosive chemicals
9.1.1. The facilities having corrosive chemicals must take measures for preventing the corrosion and protecting construction works. Factories and warehouses containing liquid corrosive chemicals must set up systems for draining, collecting and treating chemicals.
9.1.2. Materials of the equipment and pipes that contain corrosive chemicals must be suitable and ensure tightness. The valves and hatches must be safe for the operators’ movements. Pressurized equipment that contains corrosive chemicals must be checked periodically.
9.1.3. The path above the equipment that contains corrosive chemicals must have guardrails and railings to ensure safety during operation. The wall of equipment or reservoir must be at least 1.2 m higher than the position of the operator. No pedestal or any item that reduces such height shall be placed.
9.1.4. Every warehouse of corrosive chemicals must be made of materials that are not damaged by corrosive substances. The floor of the warehouse must be flat and surrounded by an edge protruding at least 0.1 m from the ground or a layer of sand that is 0.2 - 0.3 m thick;
9.2. Placing and storing corrosive chemicals
9.2.1. Organic substances (such as straw, shavings, sawdust and paper), oxidizing substances, explosive or flammable chemicals must not be stored in the same warehouse with corrosive chemicals. Acidic inorganic corrosive chemicals, alkaline corrosive substances, and other corrosive substances shall be stored in separate areas or warehouses; the aisle of storage areas must be at least 1 m wide.
9.2.2. Corrosive chemicals must be placed in the correct direction.
9.2.3. The materials of packages of corrosive chemicals must be tight and not be damaged by corrosive substances; the liquid corrosive chemicals must not be filled in a package in excess of the permissible filling factor.
9.2.4. Stacks containing corrosive chemicals must be designed and installed in such a manner as to prevent accumulation of incompatible chemicals.
9.2.5. Chemicals that are incompatible or come into contact with each other triggering hazardous reactions must not be placed in the same corrosive chemical storage area.
9.2.5.1. Regarding substances that are incompatible with corrosive substances
They must be segregated in separate areas or in the same area at a minimum distance of 5 m for liquid corrosive chemicals or 3 m for solid corrosive chemicals.
9.2.5.2. Regarding chemicals that trigger hazardous reactions when coming into contact with each other, one of the following measures should be adopted:
- Segregate them in separate areas with walls and doors to ensure safety.
- Segregate them in the same area at a minimum distance of 5 m.
- Keep them in the same area but they must not share bunding or drainage systems to ensure no contact even in the case of spills or leaks;
9.3. Working and coming into contact with corrosive chemicals
9.3.1. Corrosive chemicals must not be carried by hand. Specialized equipment shall be used when lifting, decanting or moving equipment containing corrosive chemicals.
9.3.2. The equipment and pipes that contain corrosive chemicals shall be cleaned and repaired under a safe working plan with certification by a safety officer.
9.3.3. First aid kits, taps and containers of neutralizing chemicals: NaHCO3 0.3 %, CH3COOH 0.3 % or other appropriate ones must be available where corrosive chemicals are stored in case of chemical incidents.
9.3.4. Workers in the warehouse must regularly check the tightness of the packages and containers of corrosive chemicals, and promptly take appropriate measures.
PPE must be used when coming into contact with chemicals.
10. Requirements for production, commerce, use, storage of toxic chemicals
Any facility that produces, trades, uses or stores toxic chemicals satisfying the labeling criteria corresponding to any of the pictograms GHS06, GHS07, GHS08 and GHS09 (hereinafter referred to as “toxic chemicals”) must comply with the following regulations:
10.1. Requirements concerning equipment, factories and warehouses containing toxic chemicals
10.1.1. The facility must supervise the delivery and receipt of chemicals and make a toxic chemical sales record which must indicate accurate quantity of toxic chemicals stored in the warehouse.
10.1.2. Machinery, equipment and pipes that contain toxic chemicals must be durable and tight. Air pipes must be so designed that the number of connections is minimum.
10.1.3. The danger of machinery, equipment, and special stages of manufacture must be warned using the signs.
10.1.4. Natural ventilation must be set up where toxic gases and dusts are present. Mechanical ventilation shall also be used to ensure that the concentration of toxic substances in the working environment does not exceed the maximum permissible concentration in accordance with applicable regulations.
10.1.5. The equipment containing toxic chemicals that are likely to vaporize or produce dust must be very tight and only placed in the positions required by the manufacturing process.
10.1.6. Toxic chemicals must be stored in warehouses that has watertight walls and floor, are not affected by flooding, are located far away from residential areas and firmly locked.
10.1.7. Areas where toxic chemicals are stored must have a system of collection banks and trenches; the minimum storage capacity of the collection system must be 110% of the total volume of goods;
10.2. Requirements when working and coming into contact with toxic chemicals
10.2.1. Gas masks must be used when coming into contact with toxic chemicals. Gas masks must be selected according to the chemical manufacturer's recommendations in the MSDS indicating the chemical.
10.2.2. Appropriate dust-proof face masks, dust-proof clothes, boots and gloves shall be used when being in contact with toxic dusts. The body must be tightly covered when being in contact with toxic liquids.
PPE must be placed in an airtight cabinet, have its use strictly controlled and undergo periodic inspections.
10.2.3. Pressure regulators shall be used when collecting samples under high pressure during the manufacture of toxic chemicals. Chemical-measuring devices must be attached to the equipment for manufacturing liquid toxic chemicals.
10.2.4. It is prohibited to come into direct contact with toxic chemicals. The instruments for measuring toxic chemicals must be carefully cleaned after use.
10.2.5. Before a person starts working in a tight place with toxic chemicals, the concentration of toxic chemicals in the air must be tested, appropriate measures for detoxification shall be taken to ensure that the residual amount of toxic substances is below the maximum permissible concentration and appropriate PPE must be provided. 02 or more people shall work at the same time to issue an alert or provide timely assistance in the event of an incident.
10.2.6. Decanting and repackaging areas must be airy, hygienic and safe or have a toxic gas removal system.
10.2.7. While using chemical-measuring devices, ensure that toxic chemicals are not leaked or spilled or dust is released to the air.
11. Safety requirements applicable to outdoor chemical containers
11.1. Liquid chemical storage tanks must have a bunding system and watertight floor to ensure that chemicals do not escape to the environment in the event of spills.
11.2. The storage capacity of the bunding system must be greater than or equal to 110% of the capacity of the storage tank or group of storage tanks in the dike system.
11.3. Storage tanks must be labeled with GHS pictograms. Pictograms must be visible from the entrances to the tank area.
11.3.1. For a storage tank with a diameter of 06 m or more, the edges of a pictogram must not be less than 50 cm.
11.3.2. For a storage tank with a diameter of less than 06 m, the edges of a pictogram must not be less than 15 cm.
12. Safety requirements during transportation of hazardous chemicals
12.1. Regulations set out in the Government’s Decree No. 42/2020/ND-CP dated April 08, 2020 and applicable legal documents shall be complied with when transporting hazardous chemicals.
12.2. When transporting hazardous chemicals, the following requirements must be satisfied:
12.2.1. TCVN 6304:1997 shall be complied with when moving bottles of compressed air and liquefied gases.
12.2.2. Oxygen bottles must not be transported together with bottles of flammable gases or other flammable substances.
12.2.3. When transporting hazardous chemicals, vehicles must have specialized storage tanks and must be roofed or covered. Canvas must cover all chemicals being transported to prevent exposure to rainwater and direct sunlight, and chemical leaks or spills.
12.3. Environmental conditions for storage shall be satisfied according to the MSDS.
12.4. Hazardous chemicals must not be transported together with humans, animals and other goods.
13. Safety requirements during loading and unloading of hazardous chemicals
13.1. Before hazardous chemicals are loaded onto the vehicle, the owner and the vehicle operator must check the safety of the vehicle.
13.2. Before loading or unloading, the loader must check the packages, labels, and directly provide guidance on work safety.
13.3. It is not prohibited to load chemicals that can react to each other or are extinguished using different methods onto the same vehicle. The stacks must be close together and choked to avoid collapse and movement.
13.4. After unloading part of hazardous chemicals on the vehicle, the chemicals that remain on the vehicle must be carefully choked to ensure they cannot move or collapse before carrying on the transit.
13.5. While loading or unloading, it is not permitted to drag, throw or damage goods; packages must be placed in correct direction. Hazardous chemicals must not be moved by hand.
13.6. The safety of lifting and moving instruments must be checked before loading or unloading hazardous chemicals.
1. Responsibilities of organizations and individuals
The Vietnam Chemicals Agency shall preside over and cooperate with authorities and units concerned in providing guidelines for, inspecting and supervising the implementation of this Regulation.
1.2. Departments of Industry and Trade of provinces and cities shall cooperate with authorities concerned in providing guidelines for and inspecting the implementation of this Regulation.
1.3. Hazardous chemical facilities must comply with the relevant regulations set forth in this Regulation.
2.1. This Regulation comes into force from July 01, 2021.
2.2. Within 18 months from the effective date of this Regulation, hazardous chemical facilities must satisfy the requirements laid down in this Regulation./.
PICTOGRAMS INDICATING HAZARDS OF CHEMICALS
| Pictogram under GHS | Pictograms classified and grouped based on chemical and physical properties and dangerous goods (the label is equivalent to a pictogram under GHS). | ||||||||
|
GHS01 |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
| Category 1. Explosives and explosive articles Division 1.1: Substances and articles which have a mass explosion hazard. | Category 1. Explosives and explosive articles. Division 1.2: Substances and articles which have a projection hazard but not a mass explosion hazard. | Category 1. Explosives and explosive articles. Division 1.3: Substances and articles which have a fire hazard and either a minor blast hazard or a minor projection hazard or both, but not a mass explosion hazard. | Category 1. Explosives and explosive articles. Division 1.4: Substances and articles which present no significant hazard. | Category 1. Explosives and explosive articles. Division 1.5: Very insensitive substances which have a mass explosion hazard | Category 1. Explosives and explosive articles. Division 1.6: Extremely articles which do not have a mass explosion hazard | |||
|
GHS02 |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Class 3. Flammable liquids and liquid desensitized explosives. | Class 4 Division 4.1: Flammable solids, self-reactive substances and solid explosives immersed in liquids or desensitized. | Class 4. Division 4.2.: Substances liable to spontaneous combustion | Class 4. Division 4.3: Substances which in contact with water emit flammable gases. |
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Class 2. Gases. Division 2.1: Flammable gases. | Class 5. Division 5.2: Organic peroxides |
|
|
|
| ||||
|
GHS03 |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Class 5. Division 5.1: Oxidizing substances |
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
GHS04 |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Class 2. Gases. Division 2.2: Non-flammable non-toxic gases. | Class 2. Gases. Division 2.2: Non-flammable non-toxic gases. | Class 2. Gases. Division 2.3: Toxic gases. | Class 2. Gases. Division 2.3: Oxidizing gases |
|
| ||||
|
GHS05 |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Class 8: Corrosive substances. |
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
GHS06 |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Class 6. Division 6.1: Toxic substances. | Class 2. Gases. Division 2.3: Toxic gases. |
|
|
|
| ||||
|
GHS07 | Not having an equivalent pictogram |
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
GHS08 | Not having an equivalent |
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
GHS09 | Not having an equivalent pictogram |
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Not having an equivalent pictogram |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Class 9: Miscellaneous dangerous substances and articles. |
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Not covered by the requirements concerning hazardous chemicals in the workplace |
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
| Class 6. Division 6.2: Infectious substances. | Class 7: Radioactive material. |
| ||||||
LIST OF INCOMPATIBLE CHEMICALS
Table 1: Incompatible chemicals – by pictograms

Notes:
(X) – Not compatible
(X) – Maybe compatible
Table 2: Incompatible chemicals – based on classification of dangerous goods

| Segregation key | Segregation type |
|
| COMPATIBLE: Chemicals with similar hazards are usually compatible. However chemicals may have more than one hazard and the MSDS should be still checked. |
|
| REFER TO MSDS: Separation of these chemicals may be necessary. Consult the MSDS for further guidance. MINIMUM THREE METRE (3 m) SEPERATION: These chemicals may react dangerously if stored together may and should be kept at least three metres (3 m) apart. MINIMUM THREE METRE (5 m) SEPERATION: Storing these chemicals together will significantly increase the likelihood or severity of an incident. They should be kept at least five metres (5 m) apart or in separate storage areas. ISOLATE: Dedicated storage areas or storage cabinets are recommended for self-reactive chemicals and organic peroxides, as is separation from other buildings and property boundaries. |
Table 3: Common chemical incompatibles
| No. | Chemical | Keep out of contact with |
| 1 | Acetic Acid | Chromic acid, Nitric acid, perchloric acid, peroxides, permanganates and other oxidizers |
| 2 | Acetone | Concentrated nitric and sulfuric acid mixtures, and strong bases |
| 3 | Acetylene | Chlorine, bromine, copper, fluorine, silver, mercury |
| 4 | Alkali metals | Water, carbon tetrachloride or other chlorinated hydrocarbons, carbon dioxide, the halogens |
| 5 | Ammonia, anhydrous | Mercury, chlorine, calcium hypochlorite, iodine, bromine, hydrofluoric acid |
| 6 | Ammonium nitrate | Acids, metal powders, flammable liquids, chlorates, nitrites, sulfur, finely divided organic or combustible materials |
| 7 | Aniline | Nitric acid, hydrogen peroxide |
| 8 | Arsenic materials | Any reducing agent |
| 9 | Azides | Acids |
| 10 | Bromine | Same as chlorine |
| 11 | Calcium oxide | Water |
| 12 | Carbon (activated) | Calcium hypochlorite, all oxidizing agents |
| 13 | Carbon tetrachloride | Sodium |
| 14 | Chlorates | Ammonium salts, acids, metal powders, sulfur, finely divided organic or combustible materials |
| 15 | Chromic acid and chromium trioxide | Acetic acid, naphthalene, camphor, glycerol, glycerin, turpentine, alcohol, flammable liquids in general |
| 16 | Chlorine | Ammonia, acetylene, butadiene, butane, methane, propane (or other petroleum gases), hydrogen, sodium carbide, turpentine, benzene, finely divided metals |
| 17 | Chlorine dioxide | Ammonia, methane, phosphine, hydrogen sulfide |
| 18 | Copper | Acetylene, hydrogen peroxide |
| 19 | Cumene hydroperoxide | Acids, organic or inorganic |
| 20 | Cyanides | Acids |
| 21 | Flammable liquids | Ammonium nitrate, chromic acid, hydrogen peroxide, nitric acid, sodium peroxide, halogens |
| 22 | Hydrocarbons | Fluorine, chlorine, bromine, chromic acid, sodium peroxide |
| 23 | Hydrocyanic acid | Acids |
| 24 | Hydrofluoric acid | Ammonia, aqueous or anhydrous, bases and silica |
| 25 | Hydrogen peroxide | Copper, chromium, iron, most metals or their salts, alcohols, acetone, organic materials, aniline, nitromethane, flammable liquids |
| 26 | Hydrogen sulfide | Fuming nitric acid, other acids, oxidizinggases, acetylene, ammonia (aqueous or anhydrous), hydrogen |
| 27 | Hypochlorites | Acids, activated carbon |
| 28 | Iodine | Acetylene, ammonia (aqueous or anhydrous), hydrogen |
| 29 | Mercury | Acetylene, fulminic acid, ammonia |
| 30 | Nitrate | Sulfuric acid |
| 31 | Nitric acid (concentrated) | Acetic acid, aniline, chromic acid, hydrocyanic acid, hydrogen sulfide, flammable liquids, flammable gases, copper, brass, any heavy metals |
| 32 | Nitrites | Acids |
| 33 | Nitroparaffins | Inorganic bases, amines |
| 34 | Oxalic acid | Silver, mercury |
| 35 | Oxygen | Oils, grease, hydrogen; flammable liquids, solids or gases |
| 36 | Perchloric acid | Acetic anhydride, bismuth and its alloys, alcohol, paper, wood, grease, and oils |
| 37 | Peroxides, organic | Acids (organic or mineral), avoid friction, store cold |
| 38 | Phosphorus (white) | Air, oxygen, alkalis, reducing agents |
| 39 | Potassium | Carbon tetrachloride, carbon dioxide, water |
| 40 | Potassium chlorate and perchlorate | Sulfuric and other acids, alkali metals, magnesium and calcium. |
| 41 | Potassium permanganate | Glycerin, ethylene glycol, benzaldehyde, sulfuric acid |
| 42 | Selenium | Reducing agents |
| 43 | Silver | Acetylene, oxalic acid, tartaric acid, ammonium compounds, fulminic acid |
| 44 | Sodium | Carbon tetrachloride, carbon dioxide, water |
| 45 | Sodium nitrite | Ammonium nitrate and other ammonium salts |
| 46 | Sodium peroxide | Ethyl or methyl alcohol, glacial acetic acid, acetic anhydride, benzaldehyde, carbon disulfide, glycerin, ethylene glycol, ethyl acetate, methyl acetate, furfural |
| 47 | Sulfides | Acids |
| 48 | Sulfuric acid | Potassium chlorate, potassium perchlorate, potassium permanganate (or compounds with similar light metals, such as sodium, lithium, etc.) |
| 49 | Tellurides | Reducing agents |
| 50 | Zinc powder | Sulphur |